Project Overview
Client: PM Electro-auto
Location: Nashik, Maharashtra
Application: Energy Audit and EMS system
Product: marc.desktop software (EMS)& Audit
Area: 50,000 Sq ft
Client
In the year, 1992, a group of people having more than 2 decades of expertise in sheet metal processing along with some technologists and engineers came together to form P.M.Electro-Auto Pvt Ltd.
The company was established to create high performance and high-quality press components that would cater to a dynamically evolving market. Initially, the company focused on developing its business as a OEM supplier to automobile manufacturers for their need of pressed components. Gradually, the company gained its reputation as one of the major suppliers for quality products and services, especially for the critical type press components used by the automobile manufacturers.
Premise
- The annual energy consumption of PM Electro-Auto Ltd (PMEA),Nashik is 12,74,094 KWh annually, which is drawn from Maharashtra State Electricity Board (MSEB). The utility electricity rates charged to them were 8.076 Rs./KWH, which equated to Rs 1,02,46,000 PA as their power bill.
- The energy monitoring methods were obsolete & high time consuming with low accuracy of measurement. The recorded data was not precise and time synchronized across multiple points of measurement. Analysis of data was on limited parameters and solely dependent on a person making it more prone to errors.
- PMEA plant additionally, consisted of two main compressors CPC-50 and CFM-195. The total pneumatic air generation capacity of the compressors were 194.99 cubic ft/min each. The compressor leakages were notably beneath the industrial bounds, yet energy losses were observed.
- PMEA also had two press machines of 500 ton and 700 ton. They wanted to observe the loss levels on these machines, which if proven high, could have high monetary impact. This was possible only if there was continuous monitoring of press machines for the loading and unloading conditions; as well as monitoring of all the energy related parameters.
- The power factor at the PMEA site was maintained within limit, at 1.00 but it was suspected that energy losses were occurring. This was mainly due to leading(capacitive) power factor and increased harmonics.
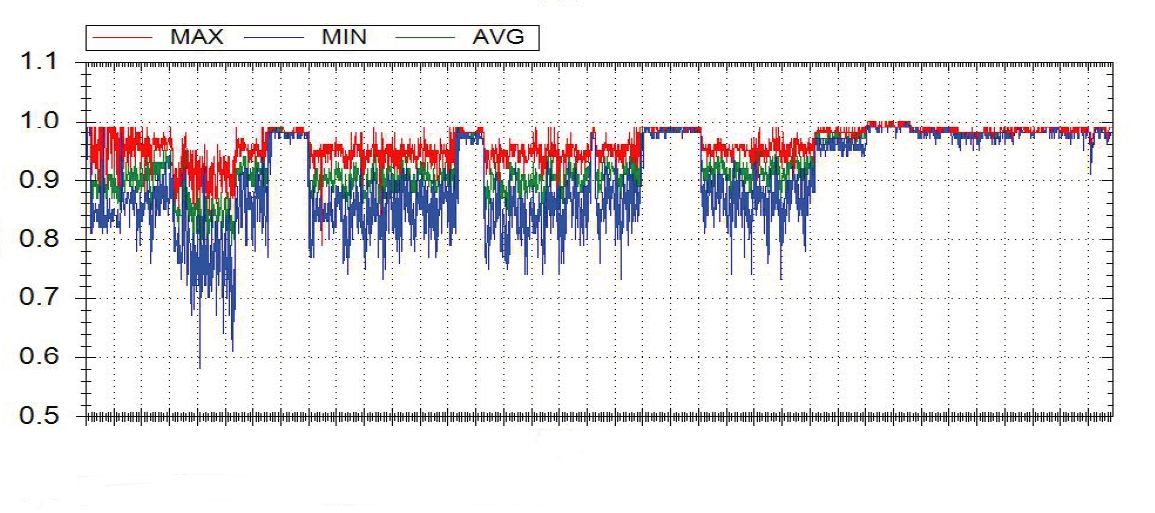
The ESL approach
Phase - I
- PMEA being an automotive plant, their significant concerns were jerk loads and fluctuating loads.
- The APFC utilized by the PMEA was designed for a balanced electrical system, consequently, the power factor was then 0.98-0.99. Due to ESL’s recommendation, the unbalanced de-tuned RTPFC system was deployed and the power factor was increased to 0.995-1.00 thus reducing energy losses.
- The air leakage was under the industry bounds (< 10%) but energy losses were perceived. These observations were because there was no automatic continuous monitoring of the loading and unloading conditions.
- ESL could additionally find scope for potential energy saving in terms of sequential operation and viability of VFD deployment.
- The suspected losses in the press machines were established after an onsite auditing round and ESL suggested VFDs for press machines as well.
- Current loading conditions revealed a slight current unbalance (~10%) resulting in losses of around 3.8%. The voltage harmonics measured were under limit and the current harmonics were above IEEE standards.
Phase - II
- ESL consulted the PMEA team to deploy an energy management system with a centralized data acquisition system.
- The advantages observed from the energy auditing study and the cost-benefit analysis showed a very quick ROI, which encouraged the PMEA team to go ahead with implementation of the EMS system.
- After implementation of ESL's energy management system, MARC, the energy-related data was logged automatically. It saved time and effort which was required for logging the data. The automatic reports & analysis on energy data additionally helped to take decision for maintaining power factor & harmonics at the desired levels that in turn resulted in the reduction of energy losses.
- EMS has been used for M&V (measurement and verification) of ESL’s suggested solution such as VFDs. The provisions of alarm and warning in the EMS allowed showing evidence for various faults. An event occurred when the motors were operating on two phases, instead of three. The system warned the authorities of the same and thus avoiding the motor damage as well avoiding plant downtime.
- By implementing MARC at PMEA, the overall energy management practices have been tightly controlled and improved.
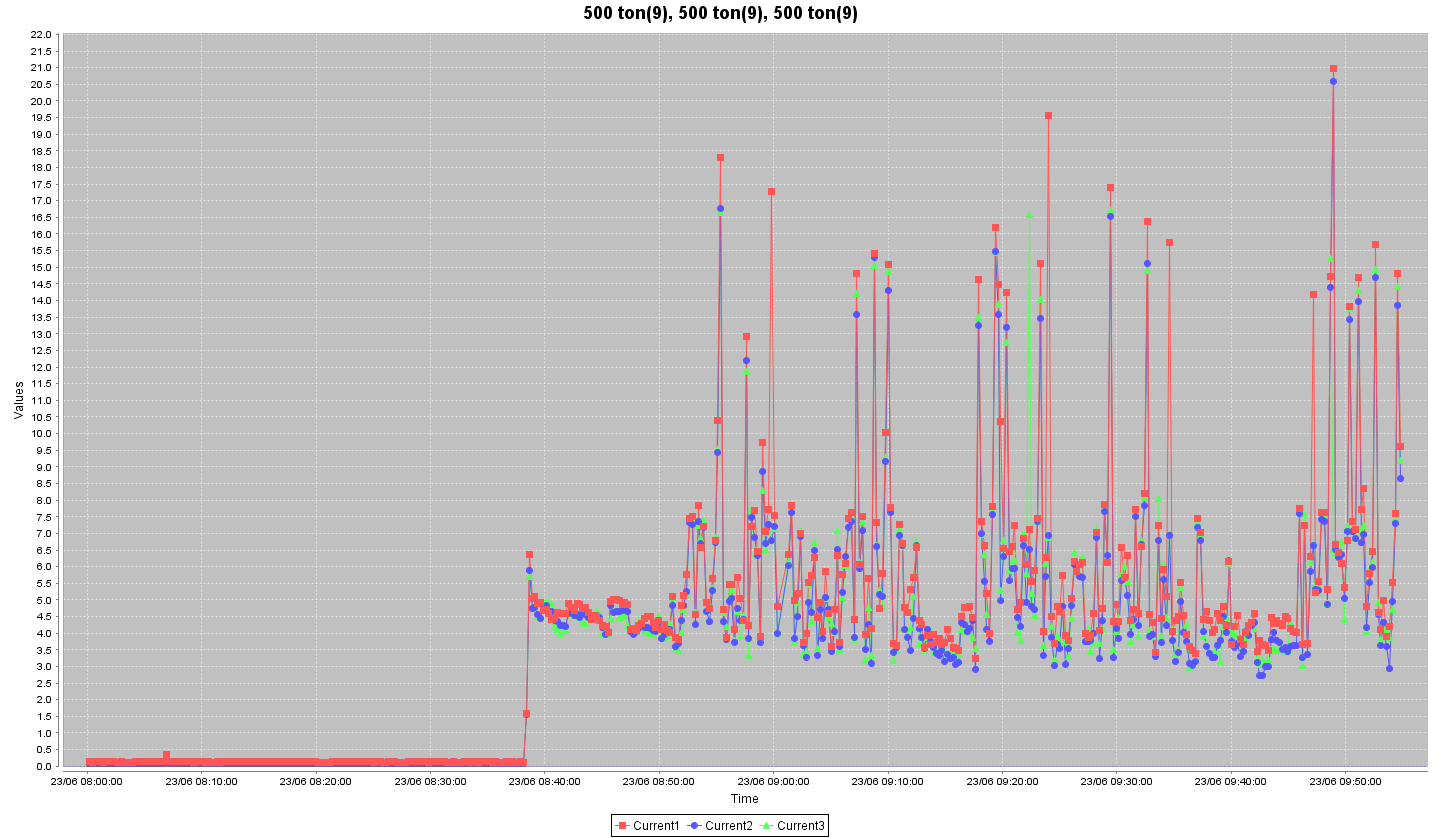
Before Implementing VFD
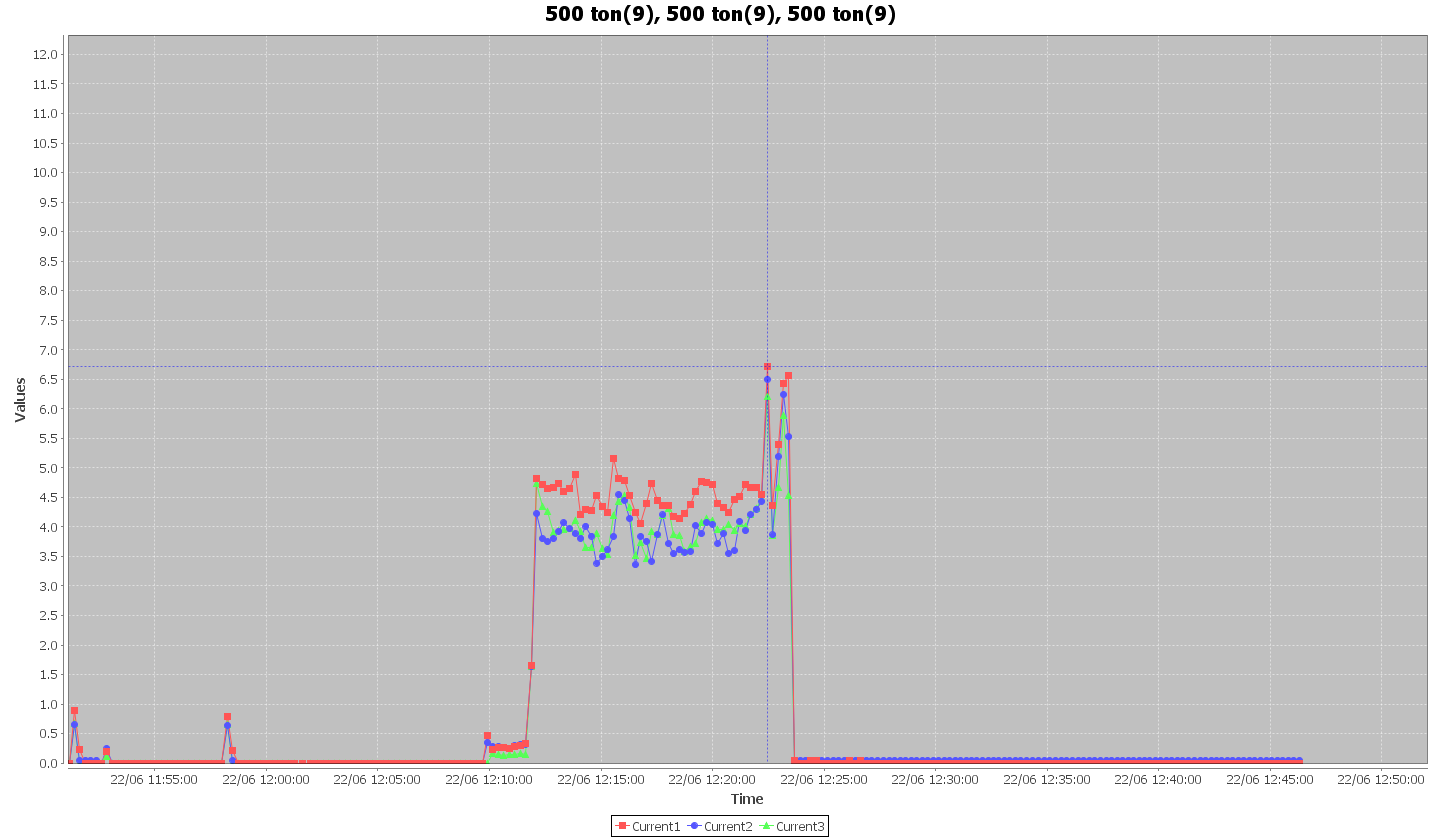
After Implementing VFD
Results
ESL’s comprehensive energy audit study highlighted the potential savings of Rs. 6,68,906 by saving 76,292 KWH units
- Installation of VFD on Compressors- The total energy saving of 17,774 KWh and an annual monetary saving of INR 1,55,698 with an estimated investment of Rs 2,27,682 and the ROI time being 17.5 months.
- Installation Of VFD on Press Machines- The total energy saving of 18,738 KWh and an annual monetary saving of INR 1,64,337 with an estimated investment of Rs 70,000 and the ROI time being 5 months.
- Installation Of VFD on 40 HP Motor- The total energy saving of 39,780 KWh and an annual monetary saving of INR 3,48,871 with an estimated investment of Rs 70,000 and the ROI time being 3 months.
157,033 KWH energy saving per year, saving INR 19,75,208 per annum.





